The VIS.X® SDK dynamically adjusts the size of an inline banner position to realize high-impact effects, such as the YOC Understitial Ad®.
To unlock the full potential of YOC, it’s advised to integrate the banner placement inside scrollable content, e.g. inside a ScrollView or RecycleView and allow resizing of the adContainer upon request.
An adContainer is needed to perform an ad call, which requires a VIS.X® Ad Unit ID (provided by YOC).
- Import the required modules
- Setup VisxViewEmitter and listen to size changes
- Integrate VisxUniversalView, to load an ad
- Adding constraints for VisxUniversalView (optional)
Import the required modules
Besides the required classes VisxUniversalView, VISX_EVENT, stopUniversal which are delivered via the module, you need to import useMemo and useState from the react module. Both are needed to listen to NativeEventEmitter which handles callbacks between React Native and the native SDK and adjust the height of the VisxUniversalView accordingly to emitted size change events.
import React, { useMemo, useState } from 'react';
import { VisxUniversalView, VISX_EVENT, stopUniversal} from '@yoc/react-native-visx-module';
Setup VisxViewEmitter and listen to size changes
As stated, the ad size will change during the run time of an ad. To listen to those changes you first have to set up VisxViewEmitter and add a Listener for the VISX_EVENT.CALLBACK_AD_SIZES to change and store height data.
const [data, setData] = useState(0);
const { VisxViewEmitter } = NativeModules;
const eventEmitter = useMemo(() => {
return new NativeEventEmitter(VisxViewEmitter);
}, [VisxViewEmitter]);
eventEmitter.addListener(VISX_EVENT.CALLBACK_AD_SIZES, (event) => {
console.log('RN VIS.X sizeChange: ' + event.auid + ' ' + event.width + 'x' + event.height);
setData(parseInt(event.height, 10));
});
Integrate VisxUniversalView, to load an ad
Once the EventEmitter is set up, you can integrate the VisxUniversalView inside your view hierarchy, to make an ad request and finally render an ad.
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<ScrollView style={{ alignSelf: 'stretch' }}>
<View
style={{
alignItems: 'center',
justifyContent: 'center',
}}
>
<Text style={{ alignSelf: 'stretch', margin: 10 }}>Some Headline</Text>
<Text style={styles.paragraph}>Some Content</Text>
<VisxUniversalView
style={{
height: data,
width: '100%',
alignSelf: 'stretch',
}}
visxAdManager={{
auid: '123456',
appDomain: 'domain-of-you-app-ads-txt.com'
}}
/>
<Text style={styles.paragraph}>Some More Content</Text>
</View>
</ScrollView>
</View>
);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
auid |
VIS.X® Ad Unit ID (provided by YOC) |
appDomain |
Domain where the app-ads.txt is located. Example: For “https://yoc.com/app-ads.txt" it would be “yoc.com” |
Adding constraints for VisxUniversalView (optional)
In case of complex app layouts, e.g. static decorative UI elements, or custom positioning of View that holds the content, you may want to constraint the position and size of where the VisxUniversalView can. The viewable part of the content View is called anchorFrame in the SDK.
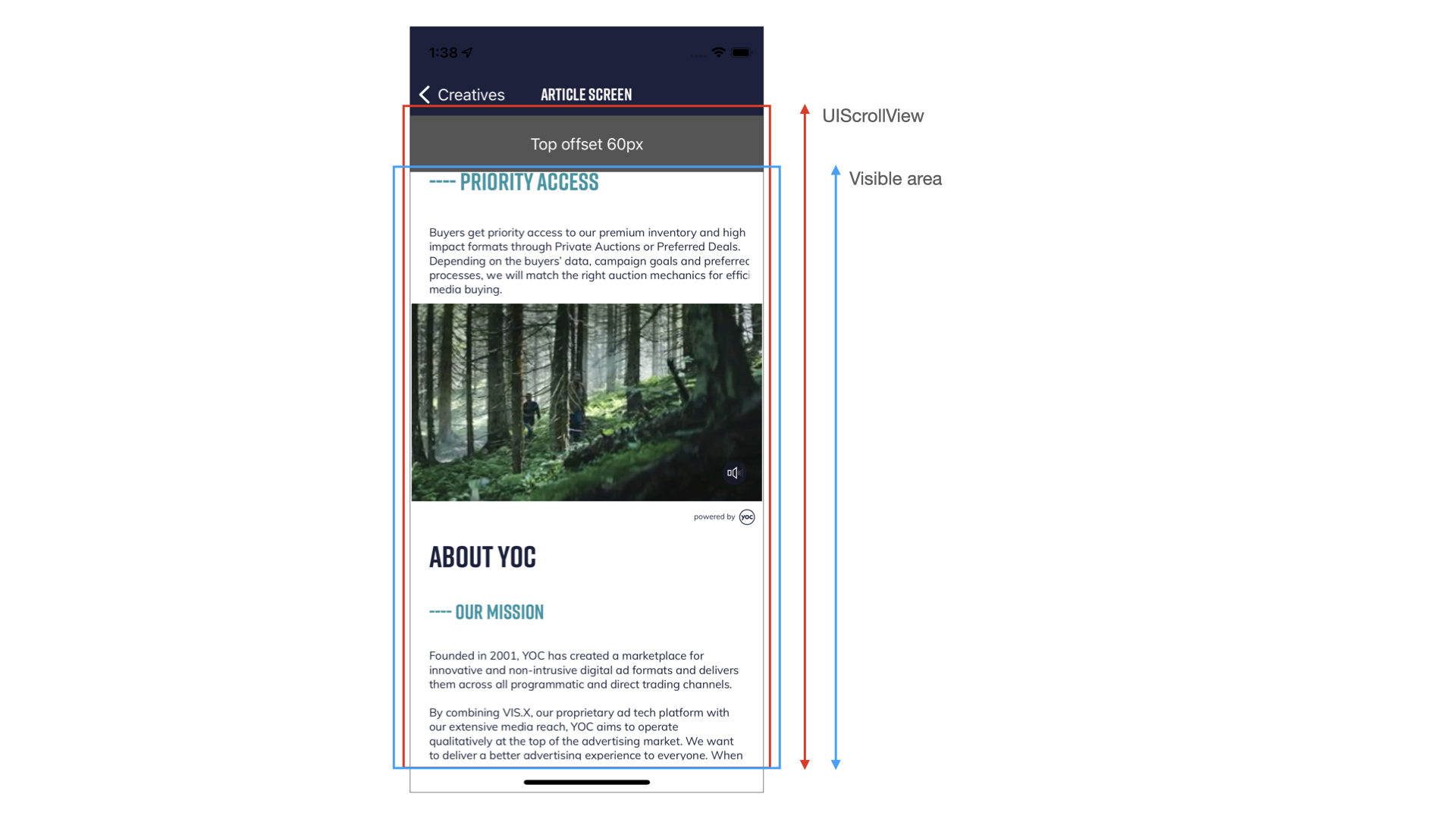
You can define the anchorFrame during the initialization using anchorX, anchorY, anchorWidth, anchorHeight as additional parameters.
<VisxUniversalView
style={{
height: data,
width: '100%',
alignSelf: 'stretch',
}}
visxAdManager={{
auid: '123456',
appDomain: 'domain-of-you-app-ads-txt.com',
anchorX: '0', //offset from left
anchorY: '94', //offset from top
anchorWidth: '390', //max width
anchorHeight: '718' //max height
}}
/>
Your inline placement is fully set up and ready for testing.
We advise you to share a build of your app with the YOC Service Team, to validate and fully test the integration together. Reach out to your contact at YOC to request test resources.